
Some studies have reportedly revealed that mood can also affect your tendency to give added significance to anchoring information.
SKEWED PERCEPTION DEFINITION HOW TO
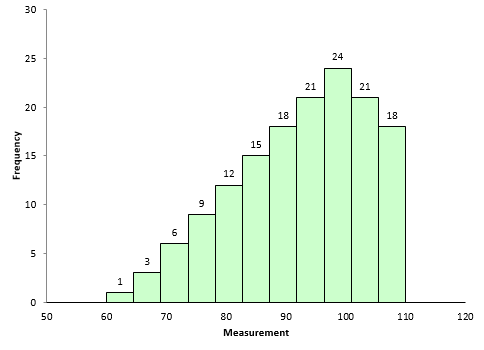
Related: How To Manage Expectations at Work (And Why It's Important) Mood Adjustments rarely make significant enough departures from their leading point of reference. The downfall of this is that sometimes, your adjustments rely too strongly on the leading value. The anchor-and-adjust hypothesis claims that when you're uncertain about a decision, you use an initial value as the basis for their future judgments. There are a few working theories about why this kind of bias occurs, including: The anchor-and-adjust hypothesis Related: Different Types of Cognitive Bias (Plus Why It's Important) Why does this kind of bias occur? Rather than viewing new information objectively, victims of bias compare any new information they receive to their reference point, which may not always be an accurate representation of a topic. Other times, bias skews your abilities to come to logical conclusions, make accurate estimates or select suitable choices. Sometimes, this can lead to more informed decision-making. What is anchoring bias?Īnchoring bias, or anchor bias, is the common inclination you have to make decisions based on previously accepted information or the first piece of information you learn about a topic. In this article, we explain what anchoring bias is and when it occurs, show you how to recognize instances of bias with examples and offer tips for overcoming anchor bias.
SKEWED PERCEPTION DEFINITION PROFESSIONAL
Understanding what this type of bias is and how it affects decisions can be important to both professional and personal development.

Noticing examples of bias can help you identify when certain factors are potentially influencing your thinking.

However, classifying and categorizing people or events can affect that way in which a story is perceived.Unconscious bias can affect decision-making, expectations and a person's perception of events. This bias can be used to understand groups and situations which are not a regular part of our lives. Readers located outside of that locale may have different reactions to the same story.Ī bias reflected by the way in which words take on different meanings depending on the context of use and the background/culture of the reader. This bias is seen when an article factors in the diversity of story through cultural and social issues. However, in real life there are complexities that may not conform to those guidelines. Source: Lora Cowell, Librarian, HUHS Library Media Center ( )Ī bias that occurs when an article is written using the who, what, when, where, why and how rubric. Reporting biases occur when an article is written with a particular tone or “spin” so that readers will perceive it in a certain way without applying skepticism or comparing the piece to other news outlets with a different ideology or perspective. Source: Lora Cowell, Librarian, HUHS Library Media Center ( ) The selection of images can skew audience perception of a story's importance and the events reported therefore, visuals are used to attract readers' attention. Media focus on stories that emphasize fear, anger, and excitement.Įditors give follow-up and clarifying stories less prominent placement because news is expected to be current and timely. A story can be "buried" by placing it in a section that is less read.Įditors select stories that draw larger audiences of readers in order to meet sponsor demands. The editorial staff decides the importance of a topic by its placement in an article.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
